Collaborative Calibration
Confidence Calibration and Rationalization for LLMs via Multi-Agent Deliberation
Anonymous Authors
Abstract
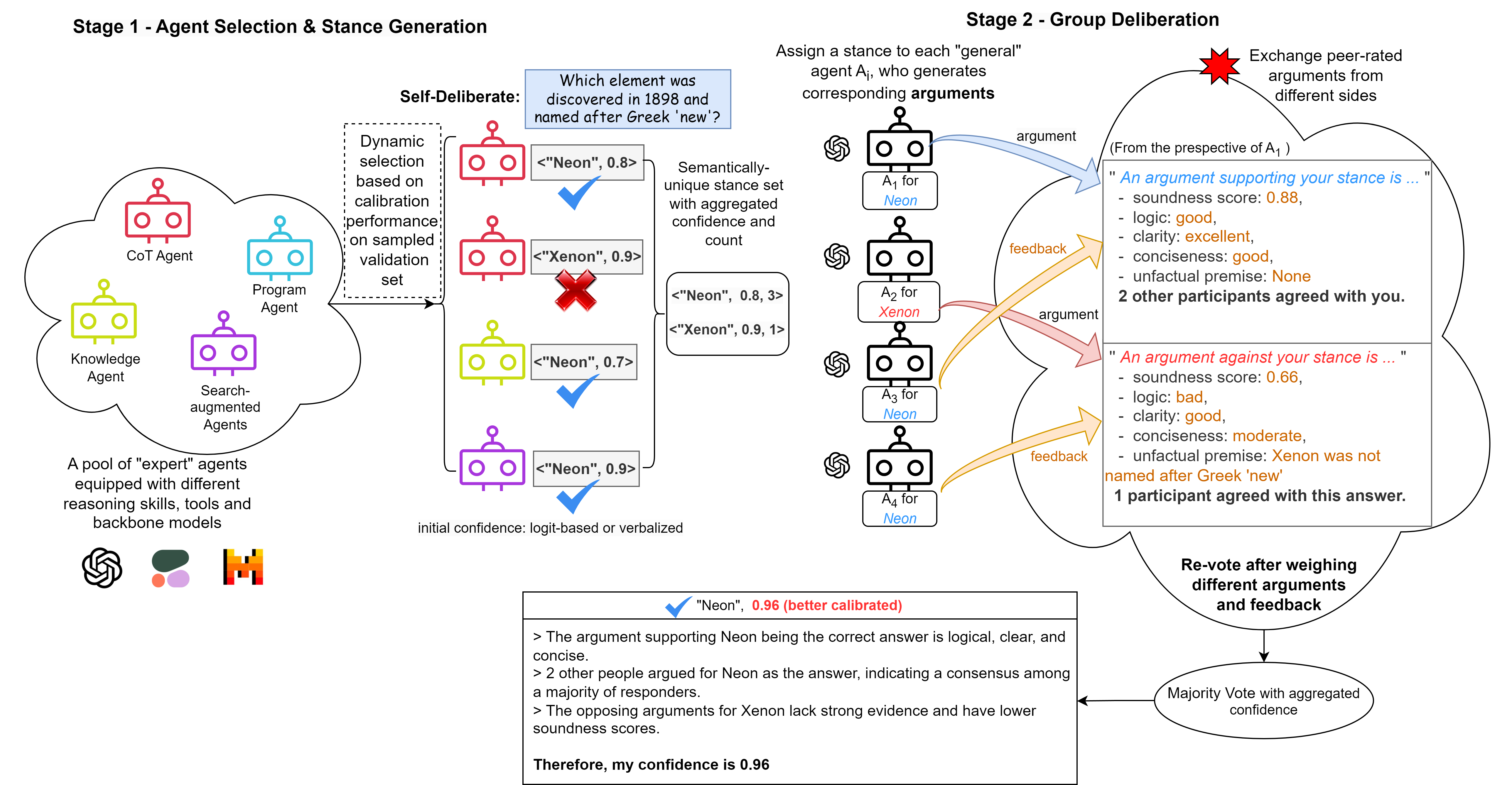
Uncertainty estimation is a significant issue for currently poorly-calibrated and generally over-confident large language models (LLMs). Unlike humans, whose decisions and confidences not only stem from intrinsic beliefs but can also be adjusted and aligned through daily observations and social interactions, existing calibration methods for LLMs focus on estimating or eliciting individual confidence without taking full advantage of the "collective wisdom": the interaction among multiple LLM agents that can collectively improve both accuracy and calibration. In this work, we propose Collaborative Calibration, a post-hoc training-free calibration strategy that leverages the collaborative and expressive capabilities of multiple tool-augmented LLM agents in a simulated group deliberation process, which not only achieves comparable results to previous methods for generative QA tasks but also harnesses the justification and rationalization of well-calibrated confidence assessments, improving the reliability of model predictions.